| New
|
Adds a new local variable or variation.
|
| Duplicate Selection
|
Makes a copy of the selected local variable or variation.
|
| Delete
|
Deletes the selected local variable or variation.
Note: Item type
variables are removed from
.
|
| Move Up
|
Moves the selected local variable or variation up one
position in this dialog's hierarchy. For variables, this controls the order in
which they appear in the
Properties dialog. For
variations, this controls the order in which they appear in lists of variations
such as that found in the
Place Parametric Cell tool.
|
| Move Down
|
Moves the selected local variable or variation down one
position in this dialog's hierarchy. For variables, this controls the order in
which they appear in the
Properties dialog. For
variations, this controls the order in which they appear in lists of variations
such as that found in the
Place Parametric Cell tool.
|
| Apply variable values to model
|
Applies the variable values of the selected variation to the
active model’s variable values.
|
| Item Type
|
Lists the available Item type libraries and item
types which are populated from the
Item Types dialog.
|
| Properties
|
The Properties section displays the properties of
the objects selected in the left-hand side of the dialog.
|
| Properties > Item Type Variable Name
|
Displays the properties of the selected item type
variable, set in the
Item Types dialog.
|
| Properties > Variables
|
Displays the currently active values of all
variables.
|
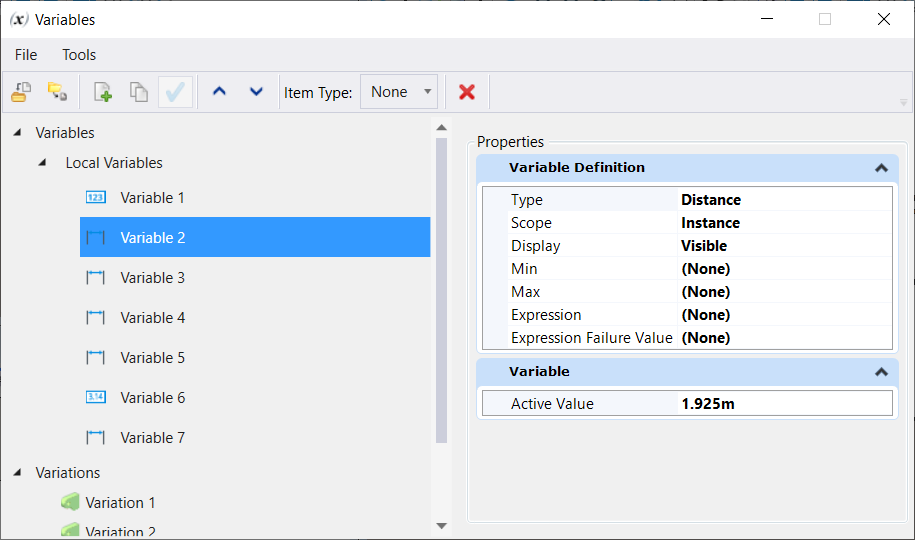
| Properties > Variable Definition
|
Displays the following parameters of the selected
local variable:
-
Type - The type of the selected
variable. The following types are supported for modeling :
- Distance - A
length quantity, defined in linear working units and displayed as specified in
the
Design File Settings dialog, Working Units category.
- Angle - An
angular quantity, defined in degrees and displayed as specified in the
Design File Settings dialog, Working Units category.
- Number - A
unit-less floating point quantity, such as a scale factor.
- Integer - A
unit-less integer quantity.
- True/False - A
boolean value which can have the value true or false. Variables of this
type can be used to control conditional expressions.
- Area - An area
defined in square of length and displayed using same units as used in
Distance.
- Text - A text
string.
Note: A
variable's type controls the types of constraints and properties with which it
can be associated. For example, all variables of type Angle will be available
in the drop-down list when defining a radius constraint.
- Expression -
Allows you to use equations to calculate the value of the variable. Expressions
may use other variables, conditional statements, arithmetic operations, and
various arithmetic and trigonometric functions. The value of a calculated
variable cannot be directly edited, but its value will update to reflect
changes made to the values of variables referenced within the expression.
Consider, for example, a simple slab that always
has its width as 0.5 times its length, and its height as 0.75 times its width.
Then Expressions could be created as follows:
When, Length=5; then, Width=0.5*Length and
Height=0.75*Width
In this case, the variables would have to be
created in the order Length, Width, and Height, as each includes a reference to
the previously defined variable. You cannot create an equation that references
a nonexistent variable, or which directly or indirectly references the variable
to which the equation is assigned. With the above variables applied to the
dimensions of the slab, only the value of Length is readily editable, but this
would cause changes to the Width and Height also.
-
Scope - Controls whether the value of
the variable can be edited when the model is placed as a parametric cell.
- Instance - A The
value of the variable can be edited during or after placement as a parametric
cell. For example, when modeling a pipe it would make sense to set the scope of
a "Length" variable to
Instance as individual pipes tend to
differ in length.
- Definition - The
value of the variable cannot be edited during or after placement as a
parametric cell. For example, when modeling a pipe you may wish to define
several variations such as "2-inch diameter pipe", "4-inch diameter pipe", etc.
In this case it would make sense to set the scope of the "Diameter" property to
Definition since pipes tend to come
in fixed diameters.
-
Display - Controls the visibility of the
variable when the model is placed as a parametric cell. Typically, intermediate
variables which are used to generate geometry but are not considered useful
outward properties of the object being modeled should be set as
Hidden.
- Visible - The
variable will be visible in the
Place Parametric Cell tool
settings, and in the
Properties dialog when
the placed cell is selected.
- Hidden - The
variable will be hidden in the
Place Parametric Cell tool
settings, and in the
Properties dialog when the
placed cell is selected.
|
| Properties > Variation
|
Displays the description and variable values for the
selected variation. You can put any desired description text for the selected
variation.
|
| Pop-up menu for Local Variables
|
Right-clicking a local variable opens a pop-up menu
with following choices:
- Rename - Allows you
to key in a new name for the selected local variable.
- Duplicate - Makes a
duplicate Copy of the selected local variable.
- Update all
variations - Applies the variable's value to all the variations.
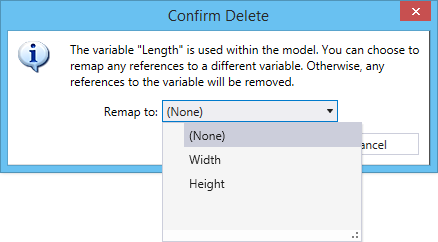
- Remap References -
Substitute another variable for this one wherever it is used in expressions or
associated to constraints or properties.
- Delete - Deletes the
selected local variable.
|
| Pop-up Menu for Variations
|
Right-clicking a variation opens a pop-up menu with
following choices:
- Apply to Model -
Applies the variable values of the selected variation set to the model in
drawing.
- Rename - Allows you
to key in a new name for the selected variation.
- Duplicate - Makes a
duplicate Copy of the selected variation.
- Delete - Deletes the
selected variation.
|
| File > Import
|
Opens the
Import Variables dialog to
import information about variables and variations from a .csv or .xlsx file
produced either by exporting into the active model or from the old Feature
Cells into the active model.
|
| File > Export
|
Opens the
Export Variables dialog to export
information about variables and variations from the active model to a .csv or
.xlsx file.
|