Condition Editor Dialog
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
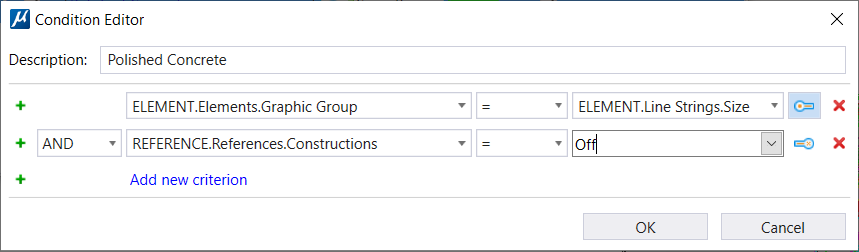
| Description | Adds description to the condition. This description displays in the Condition cell in the Display Rules dialog's list box. By default, the description is the condition that you set. You can overwrite the default description. |
| Add new criterion |
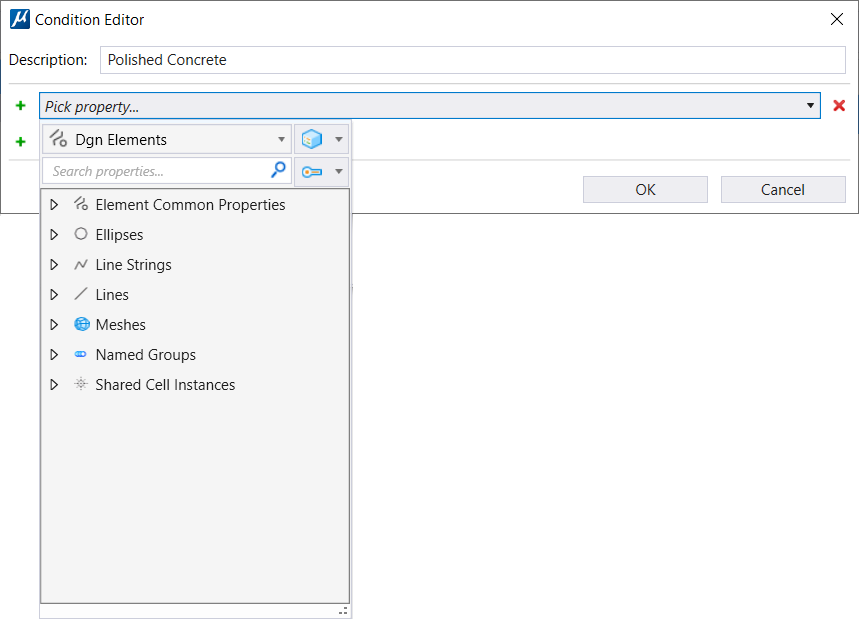
Creates a new criterion. You can select a property from the
property picker next to the icon.
Clicking the drop-down list opens the following
host property types:
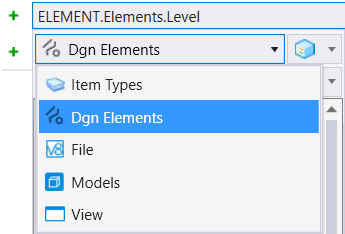
Each host property type contains one or more types. These types depend on the content of file. For example, if your file contains design, drawing, and sheet models, the Model host property type lists all three model types. If your file contains only design models, the Model host property type lists only the design model. Expanding each type lists different categories of properties. Further expanding the categories, you get the list of properties. You can also search for a particular property using the Search field. Some properties called, struct properties contain nested properties. Such properties can be expanded to select the nested properties. Each type inside a host property type contains two special properties, namely, Is Type and Is Not Type. These properties define the condition whether the selected type is available or not available respectively. Depending on the property selected, additional
drop-downs may be displayed for selecting comparison operators and setting the
values or properties. For example, if you select the level property of an
element, you will get two drop-down options. One will list the comparison
operators and the other will list all the levels.
The comparison operator drop-down list has following
special options:
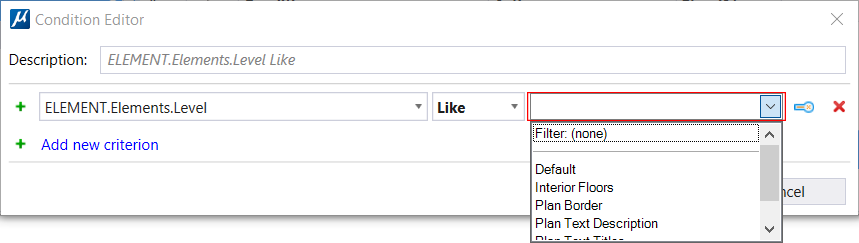
You can now use Wilds Cards in Display Rules by setting the "like" comparison followed by (*/?) to filter out properties from exhaustive lists and search the exact string. |
| Show classes for available elements | Lists all available classes. The following options are available in the drop-down: |
| Search | Lets you search for properties or classes by name. |
| Toggle between value and property comparison | Lets you add additional criteria to compare with a property or a value. You can click on this icon to switch between value and property to compare. |
| Select multiple criteria to group | (Available only when you have three or more criteria in a condition) Allows you to select more than one criterion for grouping. |
| Group selected criteria | (Available only when you select two or more Select multiple criteria to group check boxes) Groups the selected criteria. For more details, see Criteria based grouping. |
| Delete criteria | Deletes the criteria. |
Examples of Conditions for Display Rules
- You want to identify all
the elements that are of type "Room".
ELEMENT Is Room
Where,
ELEMENT - is the type of data or context object, such as element, model, file, or reference.
Is Room - is the property that identify whether the element is of type Room.
- You want to identify all
the shapes in your model that have an area greater than 20 square meters. To
achieve this, you can create the following condition in the Condition Editor
dialog:
ELEMENT.Shapes.Area > 20.000M2
Where,
ELEMENT - is the type of data or context object, such as element, model, file, or reference.
Shapes.Area - is the name of the property whose value is the area of the element.
> - Comparison operator. You can also use =, <, >, <=, >=.
20.000M2 - is the value against which the property will be compared.
- You want to identify all
the shapes in your model greater than 20 square meters and are also occupied.
To achieve this, you will have to create two criteria in the condition, as
shown below.
ELEMENT.Shapes.Area > 20.000M2
AND ELEMENT.Room.Occupied = Yes
Where,
ELEMENT - is the type of data or context object, such as element, model, file, or reference.
Shapes.Area - is the name of the property whose value is the area of the element.
> - Comparison operator. You can also use =, <, >, <=, >=.
20.000M2 - is the value against which the property will be compared.
AND - is the logical AND operator.
Room.Occupied - is the name of the property which gives the status whether the room is occupied.
Yes - is the value of the Room.Occupied property.
- You want to identify the
following:
- all shapes on floor 1 that have an area greater than 20 square meters and
- all shapes on floor 2 that have an area greater than 30 square meters
To achieve the above to criteria, you can use criteria grouping and create the following condition in Condition Editor dialog:
(
ELEMENT.Room.In floor = "1"
AND ELEMENT.Shapes.Area > 20.000SQ.M)
)
OR
(
ELEMENT.Room.In floor = "2"
AND ELEMENT.Shapes.Area > 30.000SQ.M
)
Where,
( ) - the parenthesis indicate criteria grouping.
ELEMENT - is the type of data or context object, such as element, model, file, or reference.
Room.In floor - is the name of the property whose value is the floor number of the element.
= - Comparison operator. You can also use =, <, >, <=, >=.
1 and 2 - values against which the properties will be compared.
AND and OR - is the logical AND operator.
Shapes.Area - is the name of the property whose value is the area of the element.
20.000M2 and 30.000M2 - values against which the properties will be compared.
- You have an item type that
identifies small rooms and is associated with your file, model, reference, or
view. You want to create a condition that compares the value of this item type
with the area of your rooms.
To achieve this, you can create the following condition:
ELEMENT.Shapes.Area <= MODEL.RoomThresholds.SmallRoomSize
Where,
ELEMENT - is the type of data or context object, such as element, model, file, or reference.
Shapes.Area - is the name of the property whose value is the area of the element.
<= - Comparison operator. You can also use =, <, >, >=.
MODEL - is the type of data or context object, such as element, model, file, or reference.
RoomThreshold - is the name of the item type.
SmallRoomSize - is the name of the property definition in the item type.