Group Types
The Group Types page is accessed from the Configuration tile. Click the Group Types link on the Network Metadata menu.
The Group Types page is used to define the Network Group Types and Group Relationships used within your organization. Network Groups allow a collection of network elements to be grouped together or ‘categorized’, allowing different parts of the Network to be viewed and analyzed for different functional reasons.
For example, a Group Type would be created to represent Network Routes. These Route Groups would comprise of all the network elements which when ‘chained’ together would form the Network Route. Group types such as ‘Route’ groups would be flagged as being ‘Linear’. A linear group uses the connectivity of its member elements (i.e., the End Node of one element is the Start Node of the adjoining element) to derive Offsets or SLK values along the Route.
Points of physical discontinuity along a Route, for example, at a staggered junction or intersection, may be overcome to allow ‘logical’ connectivity along the Route by the addition of Distance Breaks
The system will also cater for discontinuities caused by irregular measured distances of member network elements by created a Point of Equation at the discontinuous Node Point. A Point of Equation may be either a gap or an overlap. For more information on Points of Equation (POE) refer to the Network Manager User Guide.
Group Types may also be non-linear, such as Groups representing a geographical region or area of interest based on Inventory Items with similar attribution.
Group Types may also be defined as allowing portions of network elements to be included. These group types are known as partial groups. Partial Groups may be created as a result of a query of Inventory Items with similar attribution.
Careful planning of Group Types and Group Type hierarchies will allow reporting on a network at any level, from District or County level right through the hierarchy, down to individual Routes or parts of Routes between Intersections or Junctions for example.
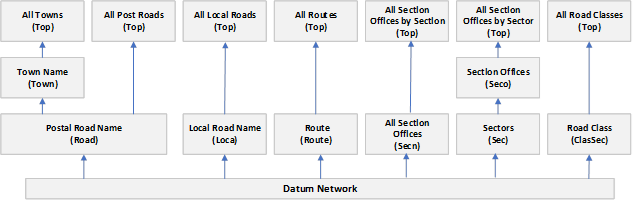
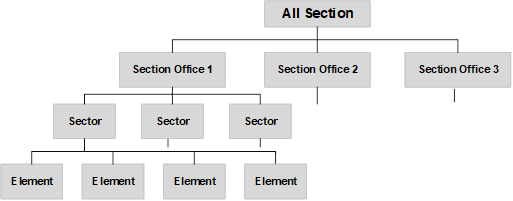
The figure below shows an example of the various levels within a group hierarchy. Examples of the Group Type Names are displayed in brackets.
Figure 22
From this example the structure of the 'All Section Offices by Sector' hierarchy may be depicted as shown below:
This hierarchy of Network Groupings would allow reporting on the entire network (All Section Offices), Individual Section Office Area (Section Office 1 etc.), Individual Sectors within a Section Office Area (Sector 1,2 etc.) or the individual network elements, which are members of the Sector Grouping.
Associating a network element to the first level of groups is carried out using Groups of Elements ( Network Manager User Guide), or through the Group creation function in Create Network Extent (Network Manager User Guide).
Additional Attributes may be defined for a Group Type using the Additional Data Types page There are two distinct types of Additional Data. ‘Primary’ Additional Data is treated as extra user defined Attributes of the Group whereas non-primary AD may be used to hold information that relates to the Group, such as Traffic Sensitivity or Reinstatement Designations.
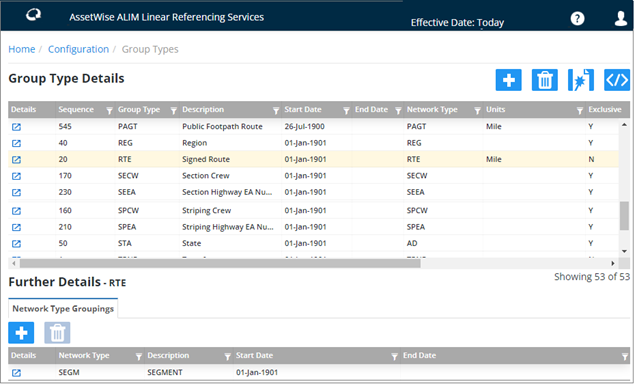
When you first enter this page, you will see all the Group Types defined in the system in a grid. Select a Group Type to display the related Network Groupings or Group Relations tabs depending if the Group allows Sub-Groups or not as explained in the following paragraphs.
To create a Group Type, click the
Group Types link on the Configuration page, and
then press the
 button at the top of the Group
Type Details page. A
Create Group Type dialog opens.
button at the top of the Group
Type Details page. A
Create Group Type dialog opens.
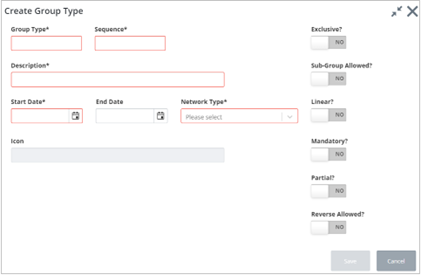
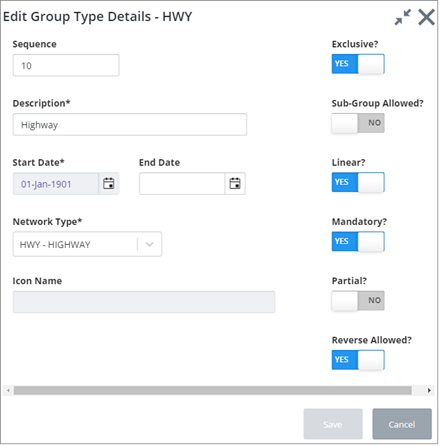
Mandatory fields are outlined in red. Enter and select the required information.
The dialog includes the following fields:
Sequence (Optional): This is used to sort the Group types in the list.
Network Type (Dropdown - Required): Enter the Network Type from which Groups of this type will derive their characteristics. This will affect such properties as the Group naming convention and units of measurement used for the Group.
Exclusive? (Yes/No switch): Set this switch to Yes if a network element, or any part of the element, may only be a member of one Group of the selected type. For example, if a network element, or any part of it, may only be a member of one Route Group the exclusivity flag should be checked.
Linear? (Yes/No switch): Set this switch to Yes if Groups of this type are linear, i.e., the member elements are connected at Node Points or by using Distance Breaks. Route Offsets or SLK values will be derived for Groups of this type. If a Group Type is flagged as ‘Linear’, the Group must be at the ‘first level’ in the hierarchy, i.e., it is a Group of Elements and cannot have Sub Groups as members.
Partial? (Yes/No switch): Set this switch to Yes if Groups of this type may contain ‘Partial’ Network Elements, i.e., the entire measured length of an element is not included in the Group membership. This may be typical of Groups created as a result of a PBI query (refer to the Asset Manager User Guide) or a Partial Network Extent. If a Group Type is flagged as ‘Partial’, the Group must be at the ‘first level’ in the hierarchy, i.e., it is a Group of Elements and cannot have Sub Groups as members.
Sub Group Allowed? (Yes/No switch): Set this switch to Yes if Groups of this type may have other groups as members, i.e., the Group is a Group of Groups. An example can be seen in Figure 22 (above), where the ‘Section Office’ group type SECN, has sub groups of type SECR as its members. The Group Types which may be Sub Groups of the selected Group Type are defined in the Group Relations window of this form.
Mandatory? (Yes/No switch): Set this switch to Yes if a Network Element of the Network Type specified in the Network Type Groupings window must belong to a Group of this Type. For example, if Elements of a Datum Network Type of ‘Classified Roads’ must belong to their ‘parent’ Route Group, the Route Group Type would be flagged as Mandatory.
Reverse Allowed? (Yes/No switch): Set this switch to Yes if a Group of this type may have member elements which do not share the same cardinality. This may occur, for example, on a route used for inspection purposes. Consider the example below where the elements shown are members of the same Inspection Route.
Click Save when finished.
To update Group Type details, on the Group Type Details page, press the
Details button
 next to the Group. The
Edit Group Type Details dialog opens.
next to the Group. The
Edit Group Type Details dialog opens.
Edit the details as required and click Save when finished.