D13.A.4 Columns
Longitudinal reinforcement for columns is calculated only from condition of strength. Longitudinal forces and bending moments in relation to local axes Yloc and Zloc are taken into account in longitudinal reinforcement calculations.
For rectangular columns the following output is generated:
-
column number;
-
column length and cross-sectional dimensions;
-
distance of centroid of each longitudinal bar from the nearest edge of the cross-section;
-
concrete class;
-
longitudinal reinforcement class;
-
range of longitudinal reinforcement bar diameters assumed in calculation;
-
diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars obtained in calculation;
-
total quantity of longitudinal bars;
-
quantity of longitudinal bars at each cross-section edge, directed parallel to the local axis Yloc ;
-
quantity of longitudinal bars at each cross-section edge, directed parallel to the local axis Zloc .
In nine columns of the table under the heading LONGITUDINAL REINFORCEMENT the following output is presented:
| Result | |
|---|---|
| Section | distance of the section from the start of the column, mm |
| Astot | total cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement, sq.cm |
| Asy | cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement bars at each edge of section, directed parallel to the local axis Yloc , sq.cm |
| Asz | cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement bars at each edge of section, directed parallel to the local axis Zloc , sq.cm |
| Percent | reinforcement percentage in the section |
| Nx, Mz, My | respective values of longitudinal force and bending moments in relation to the local axes Zloc and Yloc , determining cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement |
| Load.N. | number of loading version, determining cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement |
Diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars, total quantity of longitudinal bars as well as quantity of longitudinal bars at each edge of the section obtained from calculation should be considered as recommendation. In this case arrangement of reinforcement in the section depends on the orientation of the local axes and is as follows:

Calculated values of reinforcement cross-sectional areas are presented in the table and they may differ from recommended on the lower side.
When it is not possible according to detailing provisions to arrange in the column longitudinal reinforcement determined from calculation additional message is derived.
For columns of circular section the following output is generated:
-
column number;
-
column length and diameter of cross-section;
-
distance of centroid of each longitudinal bar to the edge of cross-section;
-
longitudinal reinforcement class;
-
assumed in calculation range of diameters of longitudinal reinforcement bars;
-
diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars obtained from calculation;
-
quantity of longitudinal bars.
In seven columns of the table under the heading LONGITUDINAL REINFORCEMENT the following results are presented:
| Section | distance of the section from the start of the column, mm |
| Astot | total cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement, sq.cm |
| Per cent | percentage of longitudinal reinforcement |
| Nx, Mz, My | respective values of longitudinal force and bending moments in relation to local axis Zloc and Yloc , determining cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement |
| Load. N. | number of loading version, determining cross-sectional area of longitudinal reinforcement |
Diameter of longitudinal reinforcement bars, total quantity of longitudinal bars as well as quantity of longitudinal bars at each edge of the section should be considered as recommendation.
Arrangement of reinforcement in section in this case is shown below:
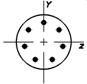
Calculated cross-sectional areas of reinforcement presented in the table may differ from recommended on the lower side.
When according to detailing provisions it is not possible to arrange in the column longitudinal reinforcement obtained from calculation additional message is derived.
