Wind pressure acting on
external surfaces is calculated from:
where
| ze | = | reference height for external pressure (see
Section 7) |
| cpe | = | pressure coefficient for external pressure
(see Section 7) |
The
"cpe"
coefficients are calculated from Table 7.1 for windward and leeward surfaces.
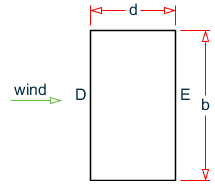
Note that windward and leeward surfaces are marked with the latter
"D" and
"E" in the figure, respectively.
| Zone |
D |
E |
| h/d |
Cpe =
Cpe,10 |
Cpe =
Cpe,10 |
| 5 |
+0.8 |
-0.7 |
| 1 |
+0.8 |
-0.5 |
| ≤ 0.25 |
+0.7 |
-0.3 |
Table 7.1 Recommended values of external pressure
coefficients for vertical walls and rectangular buildings (only partial data
for the table shown below)
The following points are important to note:
- Pressure
coefficient
"cpe" is
divided into two components: overall coefficient
"cpe,10"
(pressures on surfaces > 10 m2) and local coefficient
"cpe,1"
(pressures < 1 m2). Current implementation does not count local
effects, hence, it is assumed that
"cpe =
cpe,10". Also note that the equation given for Figure
7.2 is not implemented (i.e., interpolation of cpe between cpe,10 and cpe,1).
- In calculation
of cpe according to Table 7.1, the
following rule is applied to obtain the value of d: if the extends of the
story/stories above are greater than the extends of the current story, the
greater extends from the stories above is used.
- In calculation
of cpe according to Table 7.1, an
option to apply a correction for lack of windward and leeward correlation is
also included (see Section 7.2.2, Note (3)). In this case, the same rule
applied to cpe is followed to obtain
"d".
- The
cpe coefficients can be also directly
entered by the user. In this case, values for X and Y directions are entered
separately for windward and leeward surfaces.
- Interpolation
is applied for intermediate values of h/d in Table 7.1.

