Optimization Regions
- Break up a large optimization problem into smaller parts to keep total solution time in a reasonable range.
- Identify a specific part of the floor to be optimized. If any optimization regions are drawn, only the objects within the optimization region will be optimized. Optimizable objects outside the optimization region will be considered in the calculations but will not be optimized.
If no optimization regions are drawn, the optimizable objects in the whole slab will be optimized.
The number of optimizable objects can be displayed on this layer by selecting visible objects and on the Optimization tab check the Number of optimizable objects option. The optimization regions can also be given user defined names by selecting a region and choosing selection properties.
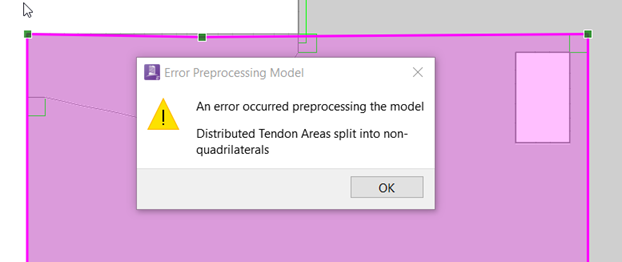
The number of objects in a single region (or whole model) is limited to 75, with a recommended maximum of 50. This can normally be achieved by drawing optimization regions of a size that might resemble a typical pour in the structure. Note that optimizable objects are not permitted to cross optimization region boundaries. During optimization preprocessing, banded tendon polylines and profile polylines will automatically be split at optimization region boundaries. Distributed tendon quadrilaterals will also automatically be split, provided that the post-split geometry results in quadrilateral shapes. If it does not, RAM Concept will provide an error message that the geometry was too complicated for automatic splitting.
Grouped tendon objects that cross optimization region boundaries will also be automatically split and regrouped according to the region in which they occur.
This can be resolved by manually manipulating the distributed tendon quadrilaterals such that they do not cross optimization boundaries, or modifying the geometry of the distributed tendon quadrilaterals and optimization regions such that splitting at the boundaries will result in quadrilateral shapes.