Concrete Behavior
This elastic modulus of concrete is defined by the user in the materials window. You can choose to use the code equation of clause 6.2.3.1 or a specified value.
- Eci = value for initial service (transfer) cross section analyses
- Ec = value for all other conditions
| = | ||
| = |
For calculations based on the "concrete section", concrete is assumed to be a perfectly linear-elastic material with no stress or strain limits.
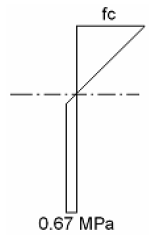
For detailed cross section analyses, three different stress strain curves are used. All three stress-strain curves are parabolic-linear curves as detailed in IS456 Fig 21. The transition strain from the parabolic to the linear curve is at 0.002.
- For initial stress conditions, the peak stress in the stress strain curve is
0.67fcui
- For service stress conditions, the peak stress in the stress-strain curve is
0.67fcu
- For strength conditions, the peak stress in the stress-strain curve is
0.67fcu / 1.5
The strength stress-strain curves are truncated at a strain of 0.0035. The other stress-strain curves have no limit strain.
Use of this curve is similar, but not technically equivalent, to the provisions of IS 456 Annex F, Fig. 28. A comparison of the stress diagrams for the Code provision and the Concept implementation are shown below:
Since RAM Concept ’s crack width design does a cracked stress analysis (with a non tension stiffened concrete stress strain curve) for the 0.8fy provision, the concrete and rebar stress results for members on which a crack width design is done will represent the range of results between the tension stiffened and the non tension stiffened concrete stress strain curve. Concrete and rebar stress results for all other members will represent use the tension stiffened concrete stress strain curve only.