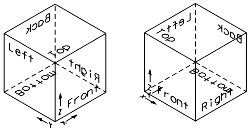
Standard Views
If you rotate a view to a standard orientation, the view orientation displays, along with the view number, in the view's title bar.
2D Views
In 2D, the design plane is parallel to the screen and, in effect, you view the model from above. The default (unrotated view) in 2D is like a Top view with its orientation such that:
- The x-axis is positive from left to right (horizontally).
- The y-axis is vertical, and positive from bottom to top (vertically).
In a 2D model, you rotate a view about an imaginary z-axis, which is perpendicular to the screen. No matter how you rotate a view in 2D, effectively, you still view it from above.
3D Orthogonal Views
In 3D, since you can rotate views about three axes, rather than just one, there are six orthogonal orientations, each of which corresponds to a standard orthogonal view: Top, Bottom, Left, Right, Front, or Back. The name of the view describes also the position from which the model is viewed.
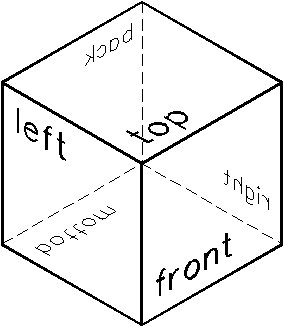
The faces of this cube correspond to the 3D orthogonal views. The cube is displayed here in an Isometric view.
A Top view displays the model from the top:
- the xy plane is parallel to your screen (as in a 2D model).
- x is positive from left to right (horizontally).
- y is positive from bottom to top (vertically).
- z is positive toward you, perpendicular to the screen.
While, for a Bottom view:
- y is positive from top to bottom (vertically).
- z is positive away from you, perpendicular to the screen.
A Front view displays the model from the front:
- the xz plane is parallel to your screen.
- x is positive from left to right (horizontally).
- z is positive from bottom to top (vertically).
- y is positive away from you, perpendicular to the screen.
While, for a Back view:
- x is positive from right to left (horizontally).
- y is positive towards you, perpendicular to the screen.
A Right view, displays the model from the right:
- the yz plane is parallel to your screen.
- y is positive from left to right (horizontally).
- z is positive from bottom to top (vertically).
- x is positive toward you, perpendicular to the screen.
While, for a Left view: