Time-Area Hydrologic Method
The time-area method of hydrologic catchment routing transforms an effective storm hyetograph into a runoff hydrograph. The method accounts for translation only and does not include storage.
Time-area method is based on the concept of time-area histogram, i.e. a histogram of contributing catchment subareas (segmentations of the catchment). To develop a time-area histogram, the catchment's time of concentration is divided into a number of time intervals. Cumulative time at the end of each time interval is used to divide the catchment into segments delimited by isochrones lines, i.e. the loci of points of equal travel time to the catchment outlet. Based on the end times of each time interval and the area of the corresponding segment the time-area histogram table can be built and used in the hydrologic routing, as shown in the following figure:
For more technical details, see "Chapter 10 Catchment Routing, Engineering Hydrology: Principle and Practice, Victor M Ponce, Prentice Hall, 1994"
- User-defined: user inputs a time and segment area (not cumulative) table
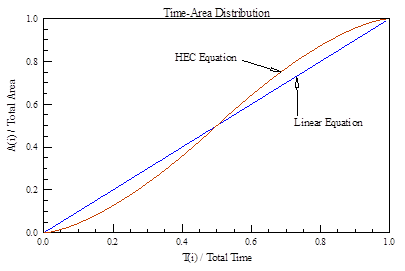
- Linear Equation: the total area is linear distributed within the total flow time or time of concentration
- HEC Equation: a synthetic time area equation was developed by US Army Corps Hydrologic Engineering Center and this selection will use the equation. Note the equation is for the cumulative area:
The following graph compares the area distributions between the linear equation and HEC equation:
Calculation Notes
The calculation methodology when using the Time-Area method varies slightly based on which loss method, time area delineation method, and area definition type are used. The decisions were made based on common usage in the industry.
with the Time-Area methods:
with the composite area definition type, the individual subareas are calculated separately, and the resultant hydrographs are consolidated to a single runoff hydrograph.
For all other cases, either subareas cannot be setup, or the subarea data will be consolidated, weighting the loss parameters based on the associated size of the subarea.