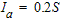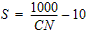SCS CN Runoff Equation
The SCS Runoff equation is used with the SCS Unit Hydrograph method to turn rainfall into runoff. It is an empirical method that expresses how much runoff volume is generated by a certain volume of rainfall.
The variable input parameters of the equation are the rainfall amount for a given duration and the basin’s runoff curve number (CN). For convenience, the runoff amount is typically referred to as a runoff volume even though it is expressed in units of depth (in., mm). In fact, this runoff depth is a normalized volume since it is generally distributed over a sub-basin or catchment area.
In hydrograph analysis the SCS runoff equation is applied against an incremental burst of rain to generate a runoff quantity. This runoff quantity is then distributed according to the unit hydrograph procedure, which ultimately develops the full runoff hydrograph.
The general form of the equation (U.S. customary units) is:
| Q | = | Runoff depth (in) | |
| P | = | Rainfall (in) | |
| S | = | Maximum retention after runoff begins (in) | |
| I a | = | Initial abstraction |
The initial abstraction includes water captured by vegetation, depression storage, evaporation, and infiltration. For any P, this abstraction must be satisfied before any runoff is possible. The universal default for the initial abstraction is given by the equation:
The ratio, 0.2, is rarely, if ever, modified.
The potential maximum retention after runoff begins, S, is related to the soil and land use/vegetative cover characteristics of the watershed by the equation:
Where the runoff curve number is developed by coincidental tabulation of soil/land use extents in the weighted runoff curve number parameter, CN.
Related Topics:
- Rational Method"Rational Method" on page 5-421
- SCS Peak Discharge"SCS Peak Discharge" on page 5-430
- Hydrograph Methods"Hydrograph Methods" on page 5-434