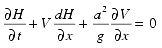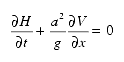Continuity Equation for Unsteady Flow
The continuity equation for a fluid is based on the principle of conservation of mass. The general form of the continuity equation for unsteady fluid flow is as follows:
The second term on the left-hand side of the preceding equation is small relative to other terms and is typically neglected, yielding the following simplified continuity equation, as used in the majority of unsteady models: